

SRS Air Bags
If the vehicle receives a strong impact from the front or side of the vehicle when the vehicle power is switched ON, the air bags inflate instantaneously and lessen the impact on the head or chest of the driver or passenger.
The SRS air bag system protects occupants together with the seat belts and they are not a substitute for the seat belts.
There are 5 types of air bags.
Vehicles with the Driver and Front Passenger Occupant Classification System have a sensor which detects an impending roll-over accident.
The air bag supplemental restraint systems are designed to provide supplemental protection in certain situations so seat belts are always important in the following ways:
Without seat belt usage, the air bags cannot provide adequate protection during an accident. Seat belt usage is necessary to:
-
Keep the occupant from being thrown into an inflating air bag.
-
Reduce the possibility of injuries during an accident that is not designed for air bag inflation, such as rear impact.
-
Reduce the possibility of injuries in frontal, near frontal or side collisions or roll-over accidents that are not severe enough to activate the air bags.
-
Reduce the possibility of being thrown from your vehicle.
-
Reduce the possibility of injuries to lower body and legs during an accident because the air bags provide no protection to these parts of the body.
-
Hold the driver in a position which allows better control of the vehicle.
Driver's front air bag
The driver's front air bag is stored in the center of the steering wheel.
When air bag crash sensors detect a frontal impact of greater than moderate force, the driver's air bag inflates quickly helping to reduce injury mainly to the driver's head or chest caused by directly hitting the steering wheel.
(With Driver and Front Passenger Occupant Classification System)
The inflation of the driver's dual-stage air bag is controlled in two energy stages depending on the driver's seat position. The driver's seat slide position sensor is located under the driver's seat. The sensor determines whether the driver's seat is forward of or behind a reference position and sends the seat position to the diagnostic module (SAS unit). The SAS unit is designed to control the deployment of the driver's air bag depending on how close the driver's seat is to the steering wheel.
During an impact of moderate severity, the driver's air bag deploys with lesser energy, whereas during more severe impacts and when the driver's seat is behind the reference position, it deploys with more energy.
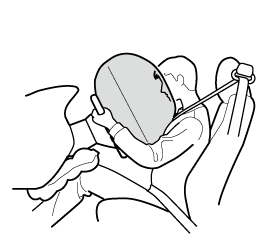
Front passenger's front air bag
The front passenger's front air bag is stored in the dashboard.
The inflation mechanism for the front passenger air bag is the same as the driver's air bag.
(With Driver and Front Passenger Occupant Classification System)
In addition, the front passenger air bag is designed to only deploy in accordance with the total seated weight on the front passenger seat.
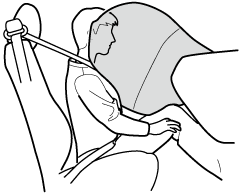
Driver and Front Passenger Knee Air Bags (Some Models)
The knee air bag is stored under the dashboard.
If the air bag crash sensors receive a frontal impact of greater than moderate force, the knee air bags deploy immediately to reduce impact to the driver and front passenger's legs.
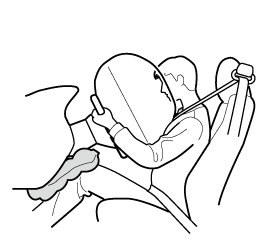
Side air bags
There are 2 types of side air bags including the side air bags for the driver and front passenger and rear passengers.
Front seat side air bags
The front seat side air bags are installed in the outboard sides of the driver and front passenger's seatbacks.
When the air bag crash sensors detect a side impact of greater than moderate force, the system inflates the side air bag only on the side in which the vehicle was hit. The side air bag inflates quickly to reduce injury to the driver or front passenger's chest caused by directly hitting interior parts such as a door or window.
(With Driver and Front Passenger Occupant Classification System)
In addition, the front passenger side air bag is designed to only deploy in accordance with the total seated weight on the front passenger seat.
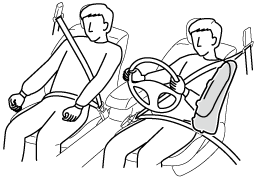
Rear seat side air bags (Some Models)
The rear seat side air bags are installed in rear pillars. The rear seat side air bags on the side where the vehicle is hit deploy regardless of whether or not an occupant is seated.
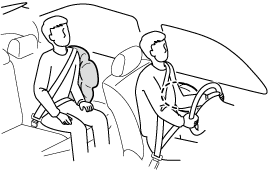
Curtain air bags
The curtain air bags are stored in the front pillars, side edges of the roof, and the rear pillars. The curtain air bag on the side where the vehicle is hit deploys regardless of whether or not an occupant is seated.
When the air bag crash sensors detect a side impact of greater than moderate force, the curtain air bag inflates quickly and helps to reduce injury mainly to the driver and front and rear outboard passengers' heads caused by directly hitting interior parts such as a door or window.
In a side impact:
Greater than moderate impact to one side of the vehicle will cause the curtain air bag on that side only to inflate.
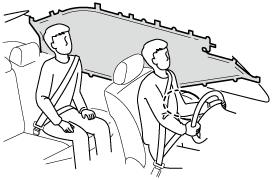
(With Driver and Front Passenger Occupant Classification System)
In a roll-over:
In response to a vehicle roll-over, both curtain air bags inflate.
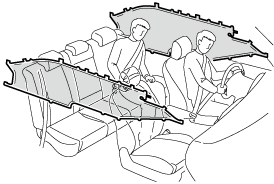
Both curtain air bags will deploy after the roll-over accident is detected.
Constant Monitoring
The following components of the air bag systems are monitored by a diagnostic system:
-
Front air bag sensors
-
Crash sensors, and diagnostic module (SAS unit)
-
Side crash sensors
-
Air bag modules
-
Seat belt pretensioners
-
Air bag/Seat belt pretensioner system warning light
-
Related wiring
(With Driver and Front Passenger Occupant Classification System)
-
Driver seat slide position sensor
-
Front passenger occupant classification sensor
-
Front passenger occupant classification module
-
Front passenger air bag deactivation indicator light
-
Front passenger seat belt buckle switch
The diagnostic module continuously monitors the system's readiness. This begins when the vehicle power is switched ON and continues while the vehicle is being driven.
